-
Resource定义
-
Resource实现
-
ByteArrayResource:
-
FileSystemResource:
-
AbstractFileResolvingResource:
-
ClassPathResource:
-
ResourceLoader定义
-
ResourceLoader实现
-
DefaultResourceLoader
-
ResourcePatternResolver
-
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
在Spring容器中,有一个基础的抽象概念:资源(Resource),其主要是对文件或类路径等资源的抽象,当对Spring容器进行初始化等操作时,会将配置文件以Resource参数对象传入给Spring容器,内部再通过ResourceLoader加载该资源,本文将比较探讨下Spring对资源的处理细节。
在Spring中,资源通过Resource接口作了基础定义:
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
/**
* 检查资源是否物理存在
*/
boolean exists();
/**
* 资源是否可读(通过getInputStream()或getFile())
*/
boolean isReadable();
/**
* 资源是否已被打开
*/
boolean isOpen();
/**
* 获取资源的URL
*/
URL getURL() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源的URI
*/
URI getURI() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源的File对象
*/
File getFile() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源内容长度
*/
long contentLength() throws IOException;
/**
* 获取资源的最近修改时间戳
*/
long lastModified() throws IOException;
/**
* 创建一个相对于当前资源的资源对象
*/
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
/**
* 资源的文件名称
*/
String getFilename();
/**
* 资源的描述信息
*/
String getDescription();
}
可以看到Resource继承自InputStreamSource,该接口定义了getInputStream()方法,用于获取资源对应的输入流对象。Spring中也提供了多种Resource实现,这可以从Resource继承树中看出:
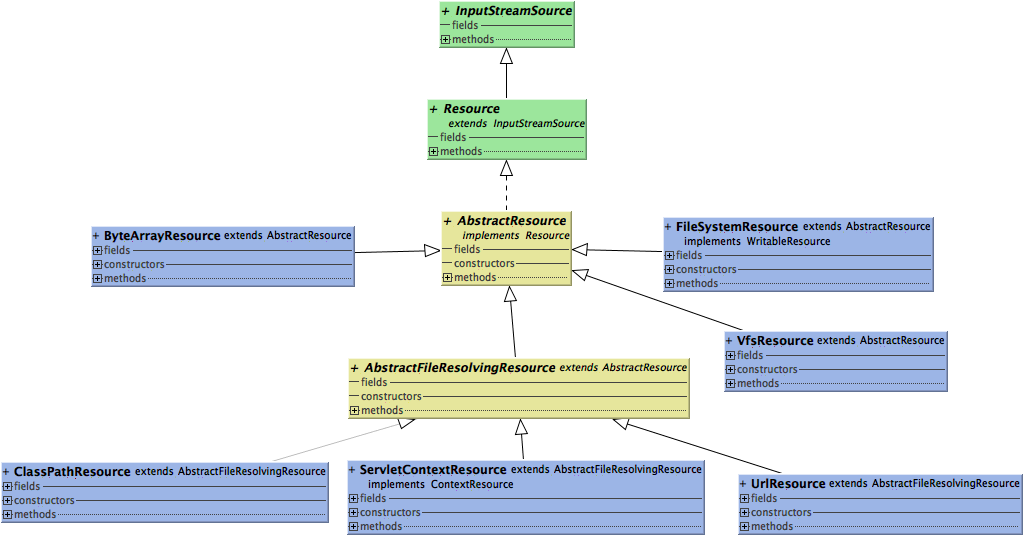
其中有我们比较熟悉的ClasspathResource(类路径资源,Main应用程序常用),FileSystemResource(文件系统资源)等,所有Resource的实现均继承自AbstractResource,其实现了一些基本功能:
public abstract class AbstractResource implements Resource {
public boolean exists() {
try {
// 先从文件系统查看文件是否存在
return getFile().exists();
} catch (IOException ex) {
// Fall back to stream existence: can we open the stream?
try {
InputStream is = getInputStream();
is.close();
return true;
}
catch (Throwable isEx) {
return false;
}
}
}
public boolean isReadable() {
return true;
}
public boolean isOpen() {
return false;
}
/**
* 需由具体子类实现
*/
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to URL");
}
public URI getURI() throws IOException {
URL url = getURL();
try {
// URL -> URI
return ResourceUtils.toURI(url);
} catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Invalid URI [" + url + "]", ex);
}
}
/**
* 需由具体子类实现
*/
public File getFile() throws IOException {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to absolute file path");
}
/**
* 通过输入流对象读取资源内容长度
*/
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
InputStream is = this.getInputStream();
Assert.state(is != null, "resource input stream must not be null");
try {
long size = 0;
byte[] buf = new byte[255];
int read;
while ((read = is.read(buf)) != -1) {
size += read;
}
return size;
} finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException ex) {
}
}
}
/**
* 最近修改时间
*/
public long lastModified() throws IOException {
long lastModified = getFileForLastModifiedCheck().lastModified();
if (lastModified == 0L) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() +
" cannot be resolved in the file system for resolving its last-modified timestamp");
}
return lastModified;
}
protected File getFileForLastModifiedCheck() throws IOException {
return getFile();
}
/**
* 需由具体子类实现
*/
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException {
throw new FileNotFoundException("Cannot create a relative resource for " + getDescription());
}
/**
* 需由具体子类实现
*/
public String getFilename() {
return null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return getDescription();
}
/**
* 通过description作比较
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (obj == this ||
(obj instanceof Resource && ((Resource) obj).getDescription().equals(getDescription())));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return getDescription().hashCode();
}
}
AbstractResource似乎并没有作太多事情,只提过一些默认实现。
/**
* 字节数组资源
*/
public class ByteArrayResource extends AbstractResource {
private final byte[] byteArray;
private final String description;
public ByteArrayResource(byte[] byteArray) {
this(byteArray, "resource loaded from byte array");
}
public ByteArrayResource(byte[] byteArray, String description) {
if (byteArray == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Byte array must not be null");
}
this.byteArray = byteArray;
this.description = (description != null ? description : "");
}
public final byte[] getByteArray() {
return this.byteArray;
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
return true;
}
@Override
public long contentLength() {
return this.byteArray.length;
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
// 构建一个ByteArrayInputStream
return new ByteArrayInputStream(this.byteArray);
}
public String getDescription() {
return this.description;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (obj == this ||
(obj instanceof ByteArrayResource && Arrays.equals(((ByteArrayResource) obj).byteArray, this.byteArray)));
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return (byte[].class.hashCode() * 29 * this.byteArray.length);
}
}
ByteArrayResource通过内部封装一个byte[],比较简单地实现了Resource。
/**
* 系统文件资源
*/
public class FileSystemResource extends AbstractResource implements WritableResource {
private final File file;
private final String path;
public FileSystemResource(File file) {
Assert.notNull(file, "File must not be null");
this.file = file;
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(file.getPath());
}
public FileSystemResource(String path) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.file = new File(path);
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
}
public final String getPath() {
return this.path;
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
return this.file.exists();
}
@Override
public boolean isReadable() {
return (this.file.canRead() && !this.file.isDirectory());
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileInputStream(this.file);
}
@Override
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
return this.file.toURI().toURL();
}
@Override
public URI getURI() throws IOException {
return this.file.toURI();
}
@Override
public File getFile() {
return this.file;
}
@Override
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
return this.file.length();
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);
return new FileSystemResource(pathToUse);
}
@Override
public String getFilename() {
return this.file.getName();
}
public String getDescription() {
return "file [" + this.file.getAbsolutePath() + "]";
}
// WritableResource 接口实现
/**
* 是否可写
*/
public boolean isWritable() {
return (this.file.canWrite() && !this.file.isDirectory());
}
/**
* 获取文件输出流
*/
public OutputStream getOutputStream() throws IOException {
return new FileOutputStream(this.file);
}
/**
* This implementation compares the underlying File references.
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
return (obj == this ||
(obj instanceof FileSystemResource && this.path.equals(((FileSystemResource) obj).path)));
}
/**
* This implementation returns the hash code of the underlying File reference.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.path.hashCode();
}
}
FileSystemResource内部包装了一个File对象,并实现了WritableResource接口,可以获取到资源的输出流进行写操作等。
AbstractFileResolvingResource作为UrlResource,ClassPathResource等的基类,主要负责将这类资源转换为File对象:
public abstract class AbstractFileResolvingResource extends AbstractResource {
@Override
public File getFile() throws IOException {
// 由子类获取资源URL
URL url = getURL();
if (url.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
// 如果是JBOSS的vfs资源
return VfsResourceDelegate.getResource(url).getFile();
}
// 解析URL为File对象
return ResourceUtils.getFile(url, getDescription());
}
@Override
protected File getFileForLastModifiedCheck() throws IOException {
URL url = getURL();
// 是否为Jar文件,包括jar, zip, vfszip, wsjar or code-source
if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(url)) {
URL actualUrl = ResourceUtils.extractJarFileURL(url);
if (actualUrl.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
return VfsResourceDelegate.getResource(actualUrl).getFile();
}
return ResourceUtils.getFile(actualUrl, "Jar URL");
}
else {
return getFile();
}
}
protected File getFile(URI uri) throws IOException {
if (uri.getScheme().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
return VfsResourceDelegate.getResource(uri).getFile();
}
return ResourceUtils.getFile(uri, getDescription());
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
try {
URL url = getURL();
if (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url)) {
// 物理文件资源
return getFile().exists();
} else {
// Try a URL connection content-length header...
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
customizeConnection(con);
HttpURLConnection httpCon =
(con instanceof HttpURLConnection ? (HttpURLConnection) con : null);
// 若是HTTP资源
if (httpCon != null) {
int code = httpCon.getResponseCode();
if (code == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {
return true;
} else if (code == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_NOT_FOUND) {
return false;
}
}
// 资源内容长度>0
if (con.getContentLength() >= 0) {
return true;
}
if (httpCon != null) {
// no HTTP OK status, and no content-length header: give up
httpCon.disconnect();
return false;
} else {
// 尝试是否可以打开输入流
InputStream is = getInputStream();
is.close();
return true;
}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public boolean isReadable() {
try {
URL url = getURL();
if (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url)) {
// 处理物理文件
File file = getFile();
return (file.canRead() && !file.isDirectory());
} else {
return true;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
return false;
}
}
@Override
public long contentLength() throws IOException {
URL url = getURL();
if (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url)) {
// 处理物理文件
return getFile().length();
} else {
// 尝试获取URL连接中的content-length头
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
customizeConnection(con);
return con.getContentLength();
}
}
@Override
public long lastModified() throws IOException {
URL url = getURL();
if (ResourceUtils.isFileURL(url) || ResourceUtils.isJarURL(url)) {
// 处理物理文件
return super.lastModified();
} else {
// 尝试获取URL连接中的last-modified头
URLConnection con = url.openConnection();
customizeConnection(con);
return con.getLastModified();
}
}
protected void customizeConnection(URLConnection con) throws IOException {
ResourceUtils.useCachesIfNecessary(con);
if (con instanceof HttpURLConnection) {
customizeConnection((HttpURLConnection) con);
}
}
protected void customizeConnection(HttpURLConnection con) throws IOException {
// 设置请求方法为HEAD
con.setRequestMethod("HEAD");
}
/**
* JBOSS vfs资源处理类
*/
private static class VfsResourceDelegate {
public static Resource getResource(URL url) throws IOException {
return new VfsResource(VfsUtils.getRoot(url));
}
public static Resource getResource(URI uri) throws IOException {
return new VfsResource(VfsUtils.getRoot(uri));
}
}
}
public class ClassPathResource extends AbstractFileResolvingResource {
private final String path;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private Class<?> clazz;
public ClassPathResource(String path) {
this(path, (ClassLoader) null);
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
String pathToUse = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
this.path = pathToUse;
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
public ClassPathResource(String path, Class<?> clazz) {
Assert.notNull(path, "Path must not be null");
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.clazz = clazz;
}
protected ClassPathResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader, Class<?> clazz) {
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.classLoader = classLoader;
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public final String getPath() {
return this.path;
}
public final ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.clazz != null ? this.clazz.getClassLoader() : this.classLoader);
}
@Override
public boolean exists() {
return (resolveURL() != null);
}
/**
* 解析path为URL
*/
protected URL resolveURL() {
if (this.clazz != null) {
return this.clazz.getResource(this.path);
} else if (this.classLoader != null) {
return this.classLoader.getResource(this.path);
} else {
return ClassLoader.getSystemResource(this.path);
}
}
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
InputStream is;
if (this.clazz != null) {
is = this.clazz.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else if (this.classLoader != null) {
is = this.classLoader.getResourceAsStream(this.path);
} else {
is = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream(this.path);
} if (is == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be opened because it does not exist");
}
return is;
}
@Override
public URL getURL() throws IOException {
URL url = resolveURL();
if (url == null) {
throw new FileNotFoundException(getDescription() + " cannot be resolved to URL because it does not exist");
}
return url;
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(this.path, relativePath);
return new ClassPathResource(pathToUse, this.classLoader, this.clazz);
}
@Override
public String getFilename() {
return StringUtils.getFilename(this.path);
}
/**
* This implementation returns a description that includes the class path location.
*/
public String getDescription() {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder("class path resource [");
String pathToUse = path;
if (this.clazz != null && !pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
builder.append(ClassUtils.classPackageAsResourcePath(this.clazz));
builder.append('/');
}
if (pathToUse.startsWith("/")) {
pathToUse = pathToUse.substring(1);
}
builder.append(pathToUse);
builder.append(']');
return builder.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (obj == this) {
return true;
}
if (obj instanceof ClassPathResource) {
ClassPathResource otherRes = (ClassPathResource) obj;
return (this.path.equals(otherRes.path) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.classLoader, otherRes.classLoader) &&
ObjectUtils.nullSafeEquals(this.clazz, otherRes.clazz));
}
return false;
}
/**
* This implementation returns the hash code of the underlying
* class path location.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return this.path.hashCode();
}
}
ClassPathResource作为较常用的资源类型,比如在初始化Spring容器时,我们通常会传入一个classpath:开头的资源,SpringSpring容器则根据这个构建一个ClassPathResource对象。
既然有了Resource,则还需要一个能加载Resource的组件,因为我们并不希望每次都都通过new的方式去构建一个Resource,这个组件叫ResourceLoader,其定义了加载资源的策略:
public interface ResourceLoader {
// classpath:前缀
String CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX = ResourceUtils.CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX;
/**
* 根据location获取资源对象,支持:
* 1. 全路径:file:C:/test.dat
* 2. 伪URL:classpath:test.dat
* 3. 相对路径:WEB-INF/test.dat
*/
Resource getResource(String location);
/**
* 暴露该ResourceLoader使用的ClassLoader
*/
ClassLoader getClassLoader();
}
同样Spring已经提供一些ResourceLoader的实现:
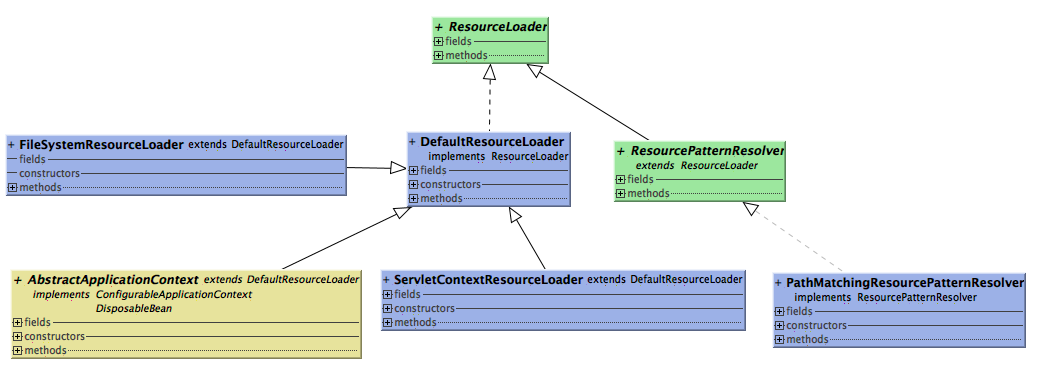
其中DefaultResourceLoader和PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver是比较常见的,也可看到AbstractApplicationContext继承自DefaultResourceLoader,继承自AbstractApplicationContext的IoC容器就已经具备加载资源的能力。
DefaultResourceLoader作为最普遍的资源加载器,可看其实现也相对简单:
/**
* 默认的资源加载器
*/
public class DefaultResourceLoader implements ResourceLoader {
private ClassLoader classLoader;
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
// 使用当前线程的类加载器
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
public DefaultResourceLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public void setClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return (this.classLoader != null ? this.classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
// 如果以classpath:开头
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
// 构建ClassPathResource对象
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// 尝试解析为URL资源
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// 解析为上下文资源
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
/**
* 类路径上下文资源: 如Servlet上下文或Portlet上下文
*/
private static class ClassPathContextResource extends ClassPathResource implements ContextResource {
public ClassPathContextResource(String path, ClassLoader classLoader) {
super(path, classLoader);
}
public String getPathWithinContext() {
return getPath();
}
@Override
public Resource createRelative(String relativePath) {
String pathToUse = StringUtils.applyRelativePath(getPath(), relativePath);
return new ClassPathContextResource(pathToUse, getClassLoader());
}
}
}
ResourcePatternResolver是对ResourceLoader的扩展,具备匹配资源模式(如Ant-Style)的功能,即将某一模式的资源location转为Resource数据,并增加了classpath*:前缀的资源解析:
public interface ResourcePatternResolver extends ResourceLoader {
// classpath*: 包括jar中的资源,这将有利于组件化
String CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX = "classpath*:";
/**
* 根据模式获取Resource数组
*/
Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException;
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver作为ResourcePatternResolver的实现,被很多地方使用,如ClassPathXmlApplicationContext容器初始化AbstractBeanDefinitionReader时,就是使用PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver作为资源加载器:
// 实例化BeanDefinitionReader
protected AbstractBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
// 初始化资源加载器
if (this.registry instanceof ResourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = (ResourceLoader) this.registry;
} else {
this.resourceLoader = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
}
...
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver如何实现资源加载:
public class PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver implements ResourcePatternResolver {
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.class);
private static Method equinoxResolveMethod;
static {
try {
// 检测Equinox OSGi
Class<?> fileLocatorClass = ClassUtils.forName("org.eclipse.core.runtime.FileLocator",
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver.class.getClassLoader());
equinoxResolveMethod = fileLocatorClass.getMethod("resolve", URL.class);
logger.debug("Found Equinox FileLocator for OSGi bundle URL resolution");
} catch (Throwable ex) {
equinoxResolveMethod = null;
}
}
private final ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
// 内部默认使用DefaultResourceLoader
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader(classLoader);
}
public ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
public ClassLoader getClassLoader() {
return getResourceLoader().getClassLoader();
}
public void setPathMatcher(PathMatcher pathMatcher) {
Assert.notNull(pathMatcher, "PathMatcher must not be null");
this.pathMatcher = pathMatcher;
}
public PathMatcher getPathMatcher() {
return this.pathMatcher;
}
public Resource getResource(String location) {
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
Assert.notNull(locationPattern, "Location pattern must not be null");
// 以classpath*:开头
if (locationPattern.startsWith(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX)) {
// 是否是一个pattern,包含*或者?
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()))) {
// 匹配查询资源
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
} else {
// 没有*或?,则不需要匹配操作,
// 通常是某个目录classpath或者某个类classpath,
// 可以是jar中的,若是jar中则会以!/作为分隔符
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
} else {
// 非classpath*:
int prefixEnd = locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1;
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
// 匹配查询资源
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
} else {
// 没有*或?,则不需要匹配操作
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
/**
* 查询所有类路径资源
*/
protected Resource[] findAllClassPathResources(String location) throws IOException {
String path = location;
if (path.startsWith("/")) {
path = path.substring(1);
}
ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
Enumeration<URL> resourceUrls = (cl != null ? cl.getResources(path) : ClassLoader.getSystemResources(path));
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
while (resourceUrls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = resourceUrls.nextElement();
result.add(convertClassLoaderURL(url));
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
protected Resource convertClassLoaderURL(URL url) {
return new UrlResource(url);
}
/**
* 通过AntPathMacher查询类路径中匹配的资源,包括jar,zip和系统文件
*/
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
// 获取匹配根目录
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
if (rootDirResource.getURL().getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
// Jboss VFS
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirResource, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
} else if (isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
// 从jar包中解析资源
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
} else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
/**
* 获取location根目录
*/
protected String determineRootDir(String location) {
int prefixEnd = location.indexOf(":") + 1;
int rootDirEnd = location.length();
while (rootDirEnd > prefixEnd && getPathMatcher().isPattern(location.substring(prefixEnd, rootDirEnd))) {
rootDirEnd = location.lastIndexOf('/', rootDirEnd - 2) + 1;
}
if (rootDirEnd == 0) {
rootDirEnd = prefixEnd;
}
return location.substring(0, rootDirEnd);
}
/**
* 解析OSGI中的bundle开头的资源
*/
protected Resource resolveRootDirResource(Resource original) throws IOException {
if (equinoxResolveMethod != null) {
URL url = original.getURL();
if (url.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) {
return new UrlResource((URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null, url));
}
}
return original;
}
/**
* 是否是jar文件资源: jar, zip, vfszip, wsjar, code-source, !/
*/
protected boolean isJarResource(Resource resource) throws IOException {
return ResourceUtils.isJarURL(resource.getURL());
}
/**
* 基于Ant-Style模式匹配找出Jar文件中配置的资源
*/
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingJarResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
URLConnection con = rootDirResource.getURL().openConnection();
JarFile jarFile;
String jarFileUrl;
String rootEntryPath;
boolean newJarFile = false;
if (con instanceof JarURLConnection) {
// 如果是JAR连接
JarURLConnection jarCon = (JarURLConnection) con;
ResourceUtils.useCachesIfNecessary(jarCon);
jarFile = jarCon.getJarFile();
jarFileUrl = jarCon.getJarFileURL().toExternalForm();
JarEntry jarEntry = jarCon.getJarEntry();
rootEntryPath = (jarEntry != null ? jarEntry.getName() : "");
} else {
// 去除!/分隔符
String urlFile = rootDirResource.getURL().getFile();
int separatorIndex = urlFile.indexOf(ResourceUtils.JAR_URL_SEPARATOR);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
jarFileUrl = urlFile.substring(0, separatorIndex);
rootEntryPath = urlFile.substring(separatorIndex + ResourceUtils.JAR_URL_SEPARATOR.length());
jarFile = getJarFile(jarFileUrl);
} else {
jarFile = new JarFile(urlFile);
jarFileUrl = urlFile;
rootEntryPath = "";
}
newJarFile = true;
}
try {
if (!"".equals(rootEntryPath) && !rootEntryPath.endsWith("/")) {
// Root entry path must end with slash to allow for proper matching.
// The Sun JRE does not return a slash here, but BEA JRockit does.
rootEntryPath = rootEntryPath + "/";
}
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(8);
// 遍历jar文件中的资源,并进行匹配
for (Enumeration<JarEntry> entries = jarFile.entries(); entries.hasMoreElements();) {
JarEntry entry = entries.nextElement();
String entryPath = entry.getName();
if (entryPath.startsWith(rootEntryPath)) {
String relativePath = entryPath.substring(rootEntryPath.length());
if (getPathMatcher().match(subPattern, relativePath)) {
result.add(rootDirResource.createRelative(relativePath));
}
}
}
return result;
} finally {
// 关闭InputStream
if (newJarFile) {
jarFile.close();
}
}
}
/**
* 解析Jar文件URL为JarFile对象
*/
protected JarFile getJarFile(String jarFileUrl) throws IOException {
if (jarFileUrl.startsWith(ResourceUtils.FILE_URL_PREFIX)) {
try {
return new JarFile(ResourceUtils.toURI(jarFileUrl).getSchemeSpecificPart());
} catch (URISyntaxException ex) {
return new JarFile(jarFileUrl.substring(ResourceUtils.FILE_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
} else {
return new JarFile(jarFileUrl);
}
}
/**
* 通过AntPathMacher查询文件系统中匹配的资源
*/
protected Set<Resource> doFindPathMatchingFileResources(Resource rootDirResource, String subPattern)
throws IOException {
File rootDir;
try {
rootDir = rootDirResource.getFile().getAbsoluteFile();
} catch (IOException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Cannot search for matching files underneath " + rootDirResource +
" because it does not correspond to a directory in the file system", ex);
}
return Collections.emptySet();
}
return doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(rootDir, subPattern);
}
/**
* 通过AntPathMacher查询文件系统中匹配的资源
*/
protected Set<Resource> doFindMatchingFileSystemResources(File rootDir, String subPattern) throws IOException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for matching resources in directory tree [" + rootDir.getPath() + "]");
}
Set<File> matchingFiles = retrieveMatchingFiles(rootDir, subPattern);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(matchingFiles.size());
for (File file : matchingFiles) {
result.add(new FileSystemResource(file));
}
return result;
}
/**
* 检索目录及子目录中匹配的文件
*/
protected Set<File> retrieveMatchingFiles(File rootDir, String pattern) throws IOException {
if (!rootDir.exists()) {
// 不存在跳过
return Collections.emptySet();
}
if (!rootDir.isDirectory()) {
// 非目录
return Collections.emptySet();
}
if (!rootDir.canRead()) {
// 不可读
return Collections.emptySet();
}
// 讲目录分隔符统一为/
String fullPattern = StringUtils.replace(rootDir.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (!pattern.startsWith("/")) {
fullPattern += "/";
}
// 配置的全路径
fullPattern = fullPattern + StringUtils.replace(pattern, File.separator, "/");
Set<File> result = new LinkedHashSet<File>(8);
// 递归获取匹配的文件
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, rootDir, result);
return result;
}
/**
* 递归获取匹配的文件
*/
protected void doRetrieveMatchingFiles(String fullPattern, File dir, Set<File> result) throws IOException {
File[] dirContents = dir.listFiles();
if (dirContents == null) {
// 空目录不处理
return;
}
for (File content : dirContents) {
String currPath = StringUtils.replace(content.getAbsolutePath(), File.separator, "/");
if (content.isDirectory() && getPathMatcher().matchStart(fullPattern, currPath + "/")) {
if (!content.canRead()) {
// 跳过不可读的目录
} else {
// 递归获取匹配的文件
doRetrieveMatchingFiles(fullPattern, content, result);
}
}
if (getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
// 匹配
result.add(content);
}
}
}
// For JBoss VFS
...
}
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver中包装了一个比较重要的路径匹配器AntPathMatcher完成了路径匹配工作,匹配规范为Ant-Style,主要匹配工作可参考AntPathMatcher.doMatch方法,具体的使用可以参照下其测试用例:
// test exact matching
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/test", "/test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/test.jpg", "test.jpg"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test", "/test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/test", "test"));
// test matching with ?'s
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("t?st", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("??st", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("tes?", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("te??", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("?es?", "test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("tes?", "tes"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("tes?", "testt"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("tes?", "tsst"));
// test matchin with *'s
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test*", "test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test*", "testTest"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test/*", "test/Test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test/*", "test/t"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test/*", "test/"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*test*", "AnothertestTest"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*test", "Anothertest"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*.*", "test."));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*.*", "test.test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*.*", "test.test.test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("test*aaa", "testblaaaa"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test*", "tst"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test*", "tsttest"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test*", "test/"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test*", "test/t"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test/*", "test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("*test*", "tsttst"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("*test", "tsttst"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("*.*", "tsttst"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test*aaa", "test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("test*aaa", "testblaaab"));
// test matching with ?'s and /'s
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/?", "/a"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/?/a", "/a/a"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/a/?", "/a/b"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/??/a", "/aa/a"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/a/??", "/a/bb"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/?", "/a"));
// test matching with **'s
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/**", "/testing/testing"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/*/**", "/testing/testing"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/**/*", "/testing/testing"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/bla/**/bla", "/bla/testing/testing/bla"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/bla/**/bla", "/bla/testing/testing/bla/bla"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/**/test", "/bla/bla/test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/bla/**/**/bla", "/bla/bla/bla/bla/bla/bla"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/bla*bla/test", "/blaXXXbla/test"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/*bla/test", "/XXXbla/test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/bla*bla/test", "/blaXXXbl/test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/*bla/test", "XXXblab/test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/*bla/test", "XXXbl/test"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/????", "/bala/bla"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/**/*bla", "/bla/bla/bla/bbb"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/**/*bla", "/bla/bla/bla"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/*bla*/**/bla/**", "/XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing/testing/"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/*bla*/**/bla/*", "/XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/*bla*/**/bla/**", "/XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing/testing"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/*bla*/**/bla/**", "/XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing/testing.jpg"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*bla*/**/bla/**", "XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing/testing/"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*bla*/**/bla/*", "XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("*bla*/**/bla/**", "XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing/testing"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("*bla*/**/bla/*", "XXXblaXXXX/testing/testing/bla/testing/testing"));
assertFalse(pathMatcher.match("/x/x/**/bla", "/x/x/x/"));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("", ""));
assertTrue(pathMatcher.match("/{bla}.*", "/testing.html"));
以上则是一些有关Spring中资源管理的小部分细节,平时还比较常用的地方就是在Spring配置文件中使用import标签:
<import resource="classpath:one-context.xml" />
<import resource="classpath*:two-context.xml" />
import时,Spring IoC容器会进一步加载resource资源,但classpath:one-context.xml会加载类路径中的查询到的第一个one-context.xml,而classpath*:two-context.xml还会加载类路径中多个jar中的two-context.xml,本质则是因为classpath:开头的资源,最终调用ClassLoader.getResource()方法,classpath*:开头的资源,最终调用ClassLoader.getResources()方法,可以将组件通过在jar包中提供一个配置文件(名字应规范,避免冲突),外部只需通过classpath:前缀import就能使用该组件。


