基础, Maven基于XML进行配置, 其配置文件叫pom.xml, 如
多模块开发
而对应的某个子模块pom.xml配置:
-
不同环境切换
项目结构如下
对应的配置文件
这样我们就可以不同环境使用不同的profile进行编译打包了:
使Spring感知到当前环境
如今很多Java项目应该都采用Maven进行构建, 其依赖管理, 配置式工作原理使得项目构建也变得比较灵活统一。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>module-name</artifactId>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<version>pacakge version</version>
<name>module-name</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<!-- jar包依赖管理-->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
...
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- 插件配置 -->
<build>
<plugins>
...
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
通常我们的项目都会有多个模块, 合理地拆分模块, 也会使得我们的项目更清晰, 更容易维护, 甚至使得模块间的依赖关系更简单, 如
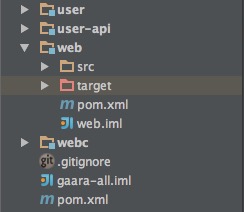
这里有4个模块, 我们会将api(如user-api)及其实现(如user)分开, 这样做对以后要 替换或扩展实现, 或者暴露给外部, 甚至作服务化时都是有好处的, web模块依赖了user和webc模块, 那么我们会有一个root pom.xml作为整个项目的配置中心
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.xxx.yyy</groupId>
<artifactId>project-all</artifactId>
<version>project-version</version>
<!-- 子模块 -->
<modules>
<module>user-api</module>
<module>user</module>
<module>web</module>
<module>webc</module>
</modules>
<packaging>pom</packaging> <!-- root模块packaging为pom类型 -->
<name>project-all</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<!-- 项目属性, 如依赖版本, 一些插件属性配置 -->
<properties>
...
</properties>
<!-- 项目依赖包管理, 子项目只需依赖对应dependency的groupId, artifactId -->
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
...
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!-- 项目插件管理 -->
<build>
<pluginManagement>
...
</pluginManagement>
</build>
<!-- 远程仓库 -->
<repositories>
<repository>
...
</repository>
</repositories>
<!-- 其他, 如发布仓库等 -->
</project>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>project-all</artifactId>
<groupId>com.xxx.yyy</groupId>
<version>project-version</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>module1</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging> <!-- module为web项目 -->
<name>module1</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<!-- 来自parent模块里的dependencyManagement中的依赖包配置 -->
<dependencies>
...
</dependencies>
<build>
<!-- 来自parent模块里的pluginManagement中的插件配置 -->
<plugins>
<plugin>
...
</plugin>
</plugins>
<!-- 环境配置, 这将实现切换环境的特性 -->
<profiles>
...
</profiles>
<!-- 其他配置 -->
...
</build>
</project>
项目开发中, 我们可能会有很多不同的环境配置, 如DB源, 服务器host等, 我们不可能每次发布都去手动更改配置, 这既繁琐又容易出错, 那基于Maven我们怎么优雅地来切换不同环境呢?如上面所说, Maven可通过profile机制和filtering机制实现环境切换, 如:
<build>
<finalName>web</finalName> <!-- war包名 -->
<resources>
<resource>
<!-- 资源目录 -->
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<!-- 开启filtering机制 -->
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
<profiles>
<!-- 默认开发环境 -->
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<build>
<filters>
<!-- 使用dev.properties -->
<filter>src/main/filter/dev.properties</filter>
</filters>
</build>
</profile>
<!-- 测试环境 -->
<profile>
<id>test</id>
<build>
<filters>
<!-- 使用test.properties -->
<filter>src/main/filter/test.properties</filter>
</filters>
</build>
</profile>
</profiles>
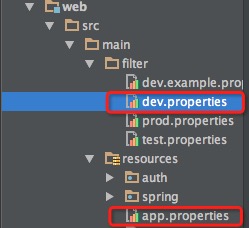
# dev.properties
env=dev
props.one=123
props.two=456
# test.properties:
env=test
props.one=123abc
props.two=456abc
# app.properties:
env=${env}
props.one=${props.one}
props.two=${props.two}
mvn clean package -Pdev
mvn clean package -Ptest
通过这种方式我们就可以灵活的切换不同的环境, 甚至可以在不同的环境切换不同的实现等。
若properties文件中有中文值出现,则会出现乱码, 猜测maven-resource-plugin读取properties文件时采用的是二进制流的方式, 查阅后发现该插件的PropertiesUtil.loadPropertyFile()方法中确实使用 FileInputStream读取properties。要解决中文乱码,可以将中文值进行 Unicode转码,或者使用Reader(如InputStreamReader)读取properties文件, 则需修改插件源码。
既然我们已经能通过maven编译打包不同的环境配置了, 那要怎么告知Spring当前是什么环境呢? 在Spring ApplicationContext对象中有一个环境配置属性environment
/** Environment used by this context; initialized by {@link #createEnvironment()} */
private ConfigurableEnvironment environment;
// 该环境配置对象通过属性spring.profiles.active来进行环境配置
/**
* Name of property to set to specify active profiles: {@value}. Value may be comma
* delimited.
* Note that certain shell environments such as Bash disallow the use of the period
* character in variable names. Assuming that Spring's {@link SystemEnvironmentPropertySource}
* is in use, this property may be specified as an environment variable as
* {@code SPRING_PROFILES_ACTIVE}.
* @see ConfigurableEnvironment#setActiveProfiles
*/
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.active";<!--若对于Web应用, 我们当然可以在初始化Spring根容器时指定该属性值, 即在web.xml中指定:-->
<context-param>
<param-name>spring.profiles.active</param-name>
<param-value>${env}</param-value> <!-- 该值会在maven打包时替换掉 -->
</context-param>
<!-- Spring Root Context -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
// 当然, 你也可以通过Java系统属性来设置
System.setProperty("spring.profiles.active", "dev");
<!--于是你就可以在Spring的配置文件里, 在不同的环境中匹配不同的配置了-->
<beans profile="dev, test">
...
</beans>
<beans profile="prod">
...
</beans>
如今, 除了Maven外, 有了更加灵活强大的构建工具Gradle, Spring已经采用了其进行构建, 其通过Groovy动态语言及编程式构建项目, 不妨也可以实践实践。


