-
接口定义
-
Environment实现
-
ConfigurableEnvironment
-
AbstractEnvironment
-
StandardEnvironment
-
StandardServletEnvironment
-
Environment初始化
-
Environment使用
-
直接使用Environment
-
profile使用
-
属性源
-
定制属性源
在日常中,经常会碰到一些环境相关的术语,也有说是上下文的,Maven中通过profile抽象出了环境配置,使开发人员可以通过不同的profile来定义不同的build上下文,Spring中也有环境一说,通过接口Enviroment来抽象,其随着Spring IoC容器的初始化而建立起来,本文将探究一番Spring运行时环境的相关细节。
Spring中将容器环境抽象为了Environment接口:
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
/**
* 获取容器激活的profile
*/
String[] getActiveProfiles();
/**
* 获取容器默认激活的profile
*/
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
/**
* 某profile是否激活,可以使用!作非逻辑,如
* env.acceptsProfiles("p1", "!p2"),若p1激活或者p2未激活,将返回true
*/
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
}
可以看到Environment定义了有关获取profile的方法,并且继承了PropertyResolver接口,该接口定义了从具体的属性源中解析属性的功能:
public interface PropertyResolver {
/**
* 检查是否有某属性
*/
boolean containsProperty(String key);
/**
* 获取某属性
*/
String getProperty(String key);
/**
* 获取某属性,不存在则返回defaultValue
*/
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
/**
* 获取某属性,其值类型为T
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 获取某属性,其值类型为T,不存在则返回defaultValue
*/
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
/**
* 获取某属性,并转换为对应的Class对象,失败会抛ConversionException
*/
<T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType);
/**
* 获取某属性,不存在抛出IllegalStateException
*/
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 获取某属性,其值类型为T,不存在抛出IllegalStateException
*/
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
/**
* 解析占位符${...}
*/
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
/**
* 解析占位符${...},不存在抛出IllegalArgumentException
*/
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
可见Spring环境主要由两个组件组成:配置(profile)和属性(property)。profile只是一个名称字符串,可对Bean容器中的Bean进行逻辑分组,即在定义Bean时,可以指定该Bean归入到某些profile中。Property则是大多应用所常见的,Spring中这些属性可以来自properties文件,JVM系统属性,系统环境变量,JNDI,Servlet上下文参数,Properties对象等。
先看下Environment继承树,比较简单直观:
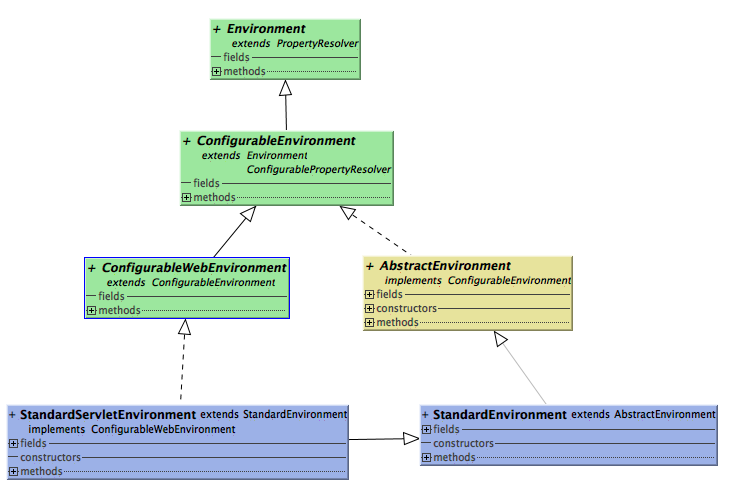
ConfigurableEnvironment主要提供对Spring容器环境的一些配置功能,并暴露了重要的getPropertySources()方法,用户可以对环境中的属性源进行更新操作等:
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
/**
* 设置激活的profile
*/
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* 添加激活的profile
*/
void addActiveProfile(String profile);
/**
* 设置默认激活的profile
*/
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles);
/**
* 获取属性源对象,通过该对象可以对属性源更新,重要的是通过addFirst,addLast等可定义属性源的优先级
*/
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources();
/**
* 获取系统环境变量
*/
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment();
/**
* 获取系统属性
*/
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties();
/**
* 1. 将parent环境激活的profile,默认的profile,属性源追加到当前child环境对象;
* 2. 若parent和child具有同名的属性源,child的属性源将被保留,parent的属性源将丢弃;
* 3. 激活和默认的profile会去掉重复的;
* 4. parent环境环境始终是不变的,任何merge后对parent环境的变化将不会影响到child环境
*/
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
}
AbstractEnvironment作为Environment的基础实现,可以设置激活的profile和默认激活的profile,具体子类主要需要提供默认的属性源对象,通过customizePropertySources()来定制属性源,而客户端应该通过getPropertySources()来定制属性源:
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
/**
* 是否忽略系统变量System.getenv(),默认为false
*/
public static final String IGNORE_GETENV_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.getenv.ignore";
/**
* 激活的profile属性名,值可以为逗号隔开的字符串
*/
public static final String ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.active";
/**
* 默认激活的profile属性名,值可以为逗号隔开的字符串
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME = "spring.profiles.default";
/**
* 默认的profile名称
*/
protected static final String RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME = "default";
protected final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass());
// 存放激活的profile集,通过LinkedHashSet保证有序且具有优先级
private final Set<String> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
// 存放默认的profile集,通过LinkedHashSet保证有序且具有优先级
private final Set<String> defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<String>(getReservedDefaultProfiles());
// 属性源对象
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources(this.logger);
// 属性解析器,内部通过迭代属性源来获取属性
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(this.propertySources);
public AbstractEnvironment() {
// 由子类定制属性源
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(format(
"Initialized %s with PropertySources %s", getClass().getSimpleName(), this.propertySources));
}
}
/**
* 由子类定制属性源
*/
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
}
/**
* 获取默认的profile名称集
*/
protected Set<String> getReservedDefaultProfiles() {
return Collections.singleton(RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME);
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
//ConfigurableEnvironment接口实现
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 获取激活的profile集
*/
public String[] getActiveProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(doGetActiveProfiles());
}
/**
* 从属性源中获取激活的profile集
*/
protected Set<String> doGetActiveProfiles() {
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
if (this.activeProfiles.isEmpty()) {
// 在属性源中找Key为spring.profiles.active的属性
String profiles = getProperty(ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
// 逗号隔开的字符串,重新设置激活的profile
setActiveProfiles(commaDelimitedListToStringArray(trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.activeProfiles;
}
}
/**
* 重新设置激活的profile
*/
public void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
// 清空之前激活的profiles
this.activeProfiles.clear();
for (String profile : profiles) {
// 验证profile名字: 非空,不能仅包含空格,不能以!开头
validateProfile(profile);
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
/**
* 添加激活的profile
*/
public void addActiveProfile(String profile) {
validateProfile(profile);
doGetActiveProfiles();
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
/**
* 获取默认的profile集
*/
public String[] getDefaultProfiles() {
return StringUtils.toStringArray(doGetDefaultProfiles());
}
/**
* 获取默认的profile集,从属性源中获取Key为spring.profiles.default的值
*/
protected Set<String> doGetDefaultProfiles() {
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
if (this.defaultProfiles.equals(getReservedDefaultProfiles())) {
String profiles = getProperty(DEFAULT_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profiles)) {
setDefaultProfiles(commaDelimitedListToStringArray(trimAllWhitespace(profiles)));
}
}
return this.defaultProfiles;
}
}
/**
* 重新设置默认profile集
*/
public void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notNull(profiles, "Profile array must not be null");
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.clear();
for (String profile : profiles) {
validateProfile(profile);
this.defaultProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
/**
* 判断某profile是否激活,若以!开头,则判断是否没有激活
*/
public boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles) {
Assert.notEmpty(profiles, "Must specify at least one profile");
for (String profile : profiles) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(profile) && profile.charAt(0) == '!') {
if (!isProfileActive(profile.substring(1))) {
return true;
}
} else if (isProfileActive(profile)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
/**
* 判断当前激活的profiles集中或默认激活的profiles中是否包含该profile
*/
protected boolean isProfileActive(String profile) {
validateProfile(profile);
Set<String> currentActiveProfiles = doGetActiveProfiles();
return (currentActiveProfiles.contains(profile) ||
(currentActiveProfiles.isEmpty() && doGetDefaultProfiles().contains(profile)));
}
/**
* 验证profile名称: 非空,不能仅包含空格,不能以!开头
*/
protected void validateProfile(String profile) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(profile)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid profile [" + profile + "]: must contain text");
}
if (profile.charAt(0) == '!') {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid profile [" + profile + "]: must not begin with ! operator");
}
}
/**
* 暴露内部的属性源,用户可以自由定制属性源
*/
public MutablePropertySources getPropertySources() {
return this.propertySources;
}
/**
* 获取系统环境变量
*/
public Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment() {
if (suppressGetenvAccess()) {
// 若Spring容易已经忽略系统环境变量
return Collections.emptyMap();
}
try {
// 返回系统变量Map对象
return (Map) System.getenv();
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getenv(attributeName);
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(format("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system " +
"environment variable [%s]; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: %s",
attributeName, ex.getMessage()));
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
/**
* Spring容器是否忽略环境变量,默认false
* 用户可以在应用classpath下配置spring.properties文件定制该属性
*/
protected boolean suppressGetenvAccess() {
return SpringProperties.getFlag(IGNORE_GETENV_PROPERTY_NAME);
}
/**
* 获取系统属性Map对象
*/
public Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties() {
try {
return (Map) System.getProperties();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
return (Map) new ReadOnlySystemAttributesMap() {
@Override
protected String getSystemAttribute(String attributeName) {
try {
return System.getProperty(attributeName);
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info(format("Caught AccessControlException when accessing system " +
"property [%s]; its value will be returned [null]. Reason: %s",
attributeName, ex.getMessage()));
}
return null;
}
}
};
}
}
/**
* 合并环境对象:包括属性源,激活profile集,默认profile集
*/
public void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent) {
// 合并属性源,通过addLast保证child属性源优先级更高
for (PropertySource<?> ps : parent.getPropertySources()) {
if (!this.propertySources.contains(ps.getName())) {
this.propertySources.addLast(ps);
}
}
// 合并激活的profile集
String[] parentActiveProfiles = parent.getActiveProfiles();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parentActiveProfiles)) {
synchronized (this.activeProfiles) {
for (String profile : parentActiveProfiles) {
this.activeProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
// 合并默认的profile集
String[] parentDefaultProfiles = parent.getDefaultProfiles();
if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(parentDefaultProfiles)) {
synchronized (this.defaultProfiles) {
// 移除掉default,parent里也有
this.defaultProfiles.remove(RESERVED_DEFAULT_PROFILE_NAME);
for (String profile : parentDefaultProfiles) {
this.defaultProfiles.add(profile);
}
}
}
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口实现,均分发给PropertyResolver处理
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
/**
* 转换服务
*/
public ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService() {
return this.propertyResolver.getConversionService();
}
public void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService) {
this.propertyResolver.setConversionService(conversionService);
}
/**
* 设置占位符前缀,默认${
*/
public void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix) {
this.propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(placeholderPrefix);
}
/*
* 设置占位符后缀,默认}
*/
public void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix) {
this.propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(placeholderSuffix);
}
public void setValueSeparator(String valueSeparator) {
this.propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(valueSeparator);
}
public void setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders) {
this.propertyResolver.setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders);
}
public void setRequiredProperties(String... requiredProperties) {
this.propertyResolver.setRequiredProperties(requiredProperties);
}
public void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException {
this.propertyResolver.validateRequiredProperties();
}
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
// PropertyResolver接口实现
//---------------------------------------------------------------------
@Override
public boolean containsProperty(String key) {
return this.propertyResolver.containsProperty(key);
}
public String getProperty(String key) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key);
}
public String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key, defaultValue);
}
public <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key, targetType);
}
public <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue) {
return this.propertyResolver.getProperty(key, targetType, defaultValue);
}
public <T> Class<T> getPropertyAsClass(String key, Class<T> targetType) {
return this.propertyResolver.getPropertyAsClass(key, targetType);
}
public String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException {
return this.propertyResolver.getRequiredProperty(key);
}
public <T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException {
return this.propertyResolver.getRequiredProperty(key, targetType);
}
public String resolvePlaceholders(String text) {
return this.propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(text);
}
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
}
StandardEnvironment比较简单,主要定制了系统属性和系统环境这两个属性源:
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
/**
* 系统变量属性源名称
*/
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
/**
* 系统属性源名称
*/
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
/**
* 定制属性源
*/
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
// 定制系统属性源
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
// 系统变量属性源
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
StandardServletEnvironment从其名称,是针对Web容器的一个环境对象:
public class StandardServletEnvironment extends StandardEnvironment implements ConfigurableWebEnvironment {
/**
* Servlet上下文属性参数属性源
*/
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletContextInitParams";
/**
* Servlet配置参数属性源
*/
public static final String SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletConfigInitParams";
/**
* jndi属性
*/
public static final String JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "jndiProperties";
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
// Servlet配置参数属性源名称
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
// Servlet上下文属性源名称
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
if (JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
// JNDI属性源
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
// 调用StandardEnvironment初始化系统属性和系统环境变量
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
public void initPropertySources(ServletContext servletContext, ServletConfig servletConfig) {
// 真实初始化Servlet的属性源
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
}
从Spring IoC容器实现中可以知道Environment的初始化发生在Bean加载之前,并在解析配置文件占位符时被实例化:
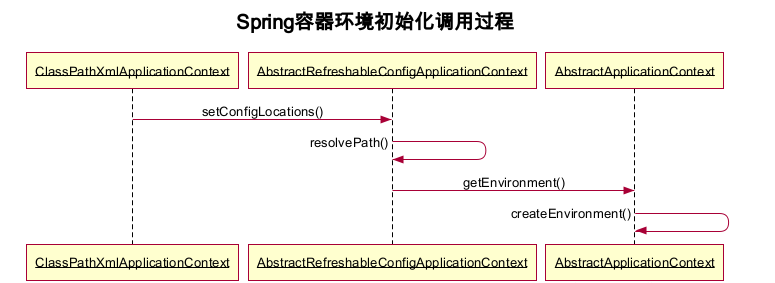
日常开发中,若想使用Environment,可以通过依赖注入或Spring中普遍的Aware回调方式:
@Autowired
private Environment env;
public class MyService implements EnvironmentAware {
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment env) {
System.out.println("EnvironmentAware callback");
}
}
之前介绍IoC容器初始化时,在DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.doRegisterBeanDefinitions()中加载XML配置文件元素时,会根据当前容器激活的环境进行加载:
// DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.doRegisterBeanDefinitions()
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// 获取beans元素的profile属性
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
// 若与容器激活环境不一致,则忽略
if (!getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
// ...
}
从前文可知,用户可以通过spring.profile.active属性激活当前容器环境,这将便于开发人员在不同的profile环境中配置不同的bean:
// 设置容器当前环境为dev,那么profile=dev的beans元素将被解析
System.setProperty(AbstractEnvironment.ACTIVE_PROFILES_PROPERTY_NAME, "dev");
<beans profile="dev">
<bean class="service.EchoService" />
</beans>
<!-- 该beans将被忽略 -->
<beans profile="prod">
<bean class="service.EchoService2" />
</beans>
上文将了Spring容器环境两个组件中的profile组件,下面将介绍其另一个组件property(属性)。
通常开发中,需要定制自己的一些属性源,如一些properties文件等,可以通过PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer配置自定义的properties属性文件:
<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:/demo.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer本质是一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,在Spring IoC容器实现中说到过,BeanFactoryPostProcessor会在所有Bean加载完之后且Bean实例化之前被调用,即在AbstractApplicationContext.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()中调用:
private void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}
// PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.postProcessBeanFactory()
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
// 合并属性文件中的KV
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// 作一些必要的转换处理
convertProperties(mergedProps);
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
// PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer.processProperties()
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props)
throws BeansException {
// 占位符解析对象
StringValueResolver valueResolver = new PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver(props);
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}
// PlaceholderConfigurerSupport.doProcessProperties()
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);
String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String curName : beanNames) {
if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);
try {
// 解析BeanDefinition中的占位符属性
visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}
// New in Spring 2.5: resolve placeholders in alias target names and aliases as well.
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
// New in Spring 3.0: resolve placeholders in embedded values such as annotation attributes.
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}
// BeanDefinitionVisitor.visitBeanDefinition()
public void visitBeanDefinition(BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
visitParentName(beanDefinition);
visitBeanClassName(beanDefinition);
visitFactoryBeanName(beanDefinition);
visitFactoryMethodName(beanDefinition);
visitScope(beanDefinition);
visitPropertyValues(beanDefinition.getPropertyValues());
ConstructorArgumentValues cas = beanDefinition.getConstructorArgumentValues();
visitIndexedArgumentValues(cas.getIndexedArgumentValues());
visitGenericArgumentValues(cas.getGenericArgumentValues());
}
通过上述BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理,BeanDefinition中的属性的值若包含占位符,将被替换为属性源中对应的属性值,当然这只是解析了bean配置中的属性,如:
<bean id="helloService" class="service.HelloService" lazy-init="true" autowire="byType">
<property name="serviceName" value="${serviceName}"/>
</bean>
而对于通过注解方式定义的属性,将会AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor注解处理器中的postProcessPropertyValues方法中注入,如:
@Value("${appName}")
private String appName;
// AbstractBeanFactory.resolveEmbeddedValue()
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(String value) {
String result = value;
for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {
if (result == null) {
return null;
}
// 利用属性源解析占位符属性
result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);
}
return result;
}
除了通过PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer注入属性,还可以通过Spring提供的util标签达到该目的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-util-3.2.xsd" profile="dev">
...
<util:properties id="app" location="app.properties" />
...
</beans>
// app.properties
mode=dev
@Value(value = "#{app.mode}")
private String mode;
与PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer不同,上面这种util:properties方式会在容器中对应注册一个名称为app的PropertiesFactoryBean,最终在注入mode字段时会通过SPEL表达式来解析。
以上则是Spring运行时环境相关的一些细节,其通过profile机制使得开发人员可以在Spring容器中隔离不同的配置,和通过属性源定制,能在程序中注入各种配置的属性,甚至通过定制PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,可以实现类似中心化配置的功能。


